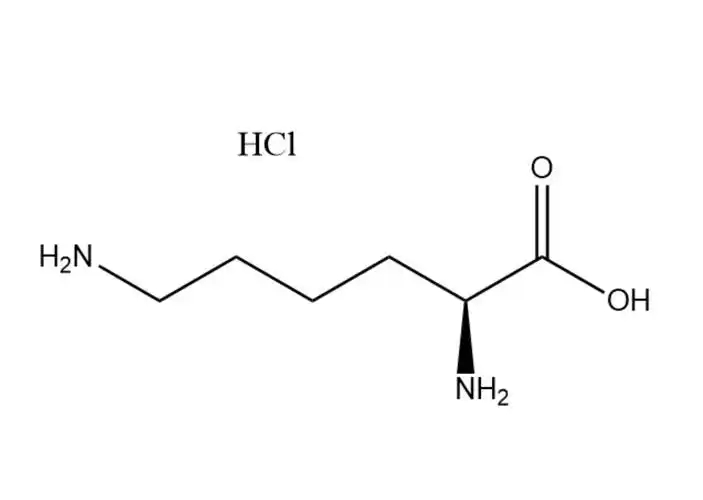
Chinese Exporter


When transporting calcium lactate gluconate, it is essential to ensure the product's safety and stability. Here are some key transportation precautions:
1. Packaging Requirements
Sealing: Ensure that the packaging of calcium lactate gluconate has good sealing properties to prevent leakage or contamination due to vibration, compression, or other factors during transportation.
Moisture Protection: As calcium lactate gluconate is sensitive to humidity, the packaging material should have moisture-resistant properties to prevent the product from absorbing moisture, clumping, or deteriorating.
Shock and Compression Resistance: For solid forms of calcium lactate gluconate (e.g., powder, tablets), the packaging should have sufficient shock and compression resistance to protect the product from damage during transportation.
2. Temperature Control
Appropriate Temperature: Calcium lactogluconate should be transported in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated environment, avoiding high temperatures. If the product requires specific temperature conditions (e.g., refrigeration), appropriate temperature control should be maintained during transportation.
Avoid Temperature Fluctuations: Efforts should be made to prevent significant temperature fluctuations during transportation, as this could affect the product's stability and quality.
3. Transportation Methods
Select Suitable Transportation: Depending on the characteristics of calcium lactate gluconate and the transportation distance, choose the appropriate means of transportation, such as by truck, train, ship, or plane. For products requiring refrigeration, use vehicles equipped with refrigeration facilities.
Secure Handling: During transportation, calcium lactogluconate should be securely fastened to prevent damage due to vehicle jolts or sudden stops.
4. Compliance with Regulations
Hazardous Materials Labeling: If calcium lactogluconate is classified as a hazardous material (though it generally is not), it must be labeled and packaged according to relevant regulations, and hazardous materials transportation regulations must be followed.
Customs Documentation: If cross-border transportation is involved, complete customs documentation should be prepared, and the product must comply with the import regulations and standards of the destination country.
5. Emergency Measures
Leakage Management: In the event of a product leakage, appropriate emergency measures should be taken immediately, such as using absorbent materials to clean up the spill and properly disposing of waste.
Incident Reporting: If an accident or abnormal situation occurs during transportation, it should be reported to the relevant authorities promptly, and the emergency plan should be followed.
In summary, transporting calcium lactate gluconate requires attention to packaging requirements, temperature control, transportation methods, regulatory compliance, and emergency measures. By taking appropriate actions, the safety and stability of the product during transportation can be ensured.
Другие товары поставщика
|
|
calcium hydrogen phosphate |
The reviews of calcium hydrogen phosphateproducts can vary depending on the intended use, industry, and specific requirements of users.
In the food... |
|
|
Ferric sodium edetate |
|
|
|
Magnesium citrate granule |
Magnesium citrate granule is a chemical preparation obtained by the complete neutralization of citric acid and high purity magnesium source, and th... |
|
|
Calcium lactate gluconate |
Calcium lactate gluconate manufacturers in China can offer several production advantages, making them competitive players in the global market for ... |
|
|
High-quality Magnesium Citrate Granules |
Product Name:Magnesium Citrate Granules
Description
Raw material :Magnesium Citrate, Corn Starch, Microcrystalline Cellulose, PVP (K30)
Mg Assay(we... |
Все товары поставщика
Похожие товары