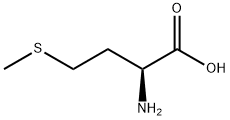
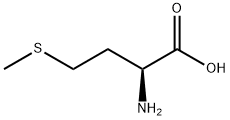
L-Methionine
L-Methionine, an essential sulfur-containing amino acid, cannot be endogenously synthesized by humans and most monogastric animals (e.g., chickens, pigs) and must be obtained through dietary intake, nutritional supplements, or fortified products. Its sources are primarily categorized into natural dietary sources, industrial production (for additives), and specialized nutritional formulations. L-methionine sources range from natural foods (animal-derived as primary, plant-based as secondary) to industrial production (chemical synthesis and biofermentation for additives) and specialized nutritional products. The choice of source depends on dietary preferences, physiological needs, and application scenarios (human nutrition vs. animal feed).
Other supplier products
|
|
DL-Methionine |
DL-Methionine, chemically designated asDL-2-amino-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid, is a racemic mixture consisting of equimolar quantities of L-methion... |
|
|
L-Methionine |
Dietary Sources and Applications of L-Methionine Dietary Sources: Rich in animal-derived foods such as meat (beef, pork), fish, eggs, and dairy pro... |
|
|
DL-methionine |
The carboxyl group in DL-methionine can undergo esterification, amidation, and decarboxylation reactions under specific conditions.Esterification r... |
|
|
DL-Alanine |
DL-Alanine is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory bodies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safet... |
|
|
L-Methionine powder |
L-Methionine is essential for the development and function of immune cells: It promotes the synthesis of antibodies (immunoglobulins) and cytokines... |
供应产品
Same products
|
|
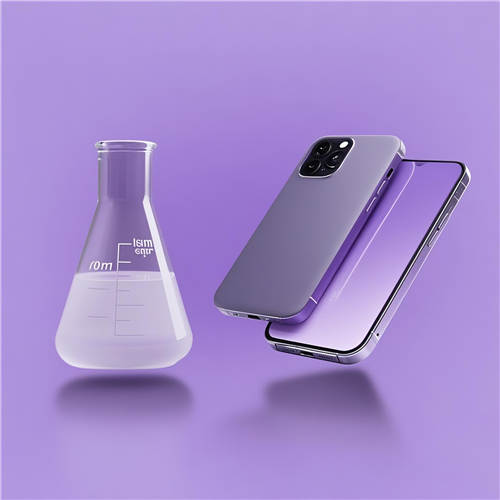
Easy-cleaning Silicone-Modified Waterborne UV Resin |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
LUV533 is a high-performance, silicone-modified hexafunctional waterborne UV resinengineered to d... |
|
|
Water-based Soft-Touch Resin for Consumer Electronics |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
Water-based Soft-Touch Resinis an advanced coating material formulated to deliver a luxurious, ve... |
|
|
Conformal Coatings |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
The conformal coatingsprovide good adhesion to metal, PCB and other substrates after curing at ro... |
|
|
Metalized & Laser Transfer coating |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
Metallized and laser transfer coatingsare designed with sustainability in mind, ensuring minimal ... |
|
|
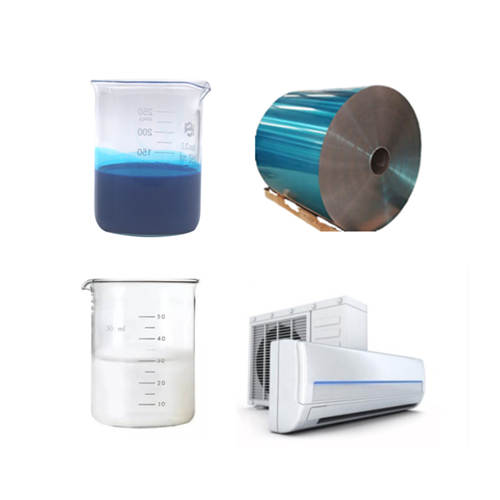
Hydrophilic coatings for Air Conditioner |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
A water-based coating combination applied on the surface of aluminum foil, which forms a layer wi... |