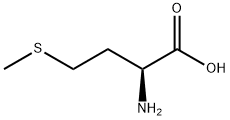
L-Methionine


Core Biological Functions of L-Methionine Protein Synthesis Precursor: As an essential amino acid, L-Methionine is a fundamental building block for protein synthesis, participating in the formation of structural proteins (e.g., muscle fibers) and functional proteins (e.g., enzymes, antibodies) in organisms. It initiates the translation process of protein synthesis by acting as the N-terminal amino acid of nascent peptide chains. Methyl Group Donor: The methylthio group in L-Methionine can be activated to form S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), a universal methyl donor in biological systems. It participates in over 100 methyltransferase-catalyzed reactions, regulating the synthesis and metabolism of nucleic acids (DNA/RNA methylation), lipids (cholesterol biosynthesis), neurotransmitters (epinephrine, choline synthesis), and hormones (thyroid hormone activation), thereby influencing gene expression, cell signaling, and metabolic balance. Antioxidant Defense: L-Methionine is a precursor for glutathione (GSH) synthesis—after conversion to cysteine via transsulfuration, it combines with glutamate and glycine to form GSH, a key intracellular antioxidant. GSH scavenges reactive oxygen species (ROS), protects cell membranes from oxidative damage, and maintains the activity of antioxidant enzymes (e.g., glutathione peroxidase). Lipid Metabolism Regulation: It promotes fatty acid oxidation and inhibits fat accumulation in the liver by participating in the synthesis of carnitine (a molecule that transports fatty acids into mitochondria for energy production). This helps prevent fatty liver disease and regulates cholesterol metabolism by facilitating the conversion of homocysteine to cysteine, reducing the risk of hyperhomocysteinemia-related cardiovascular issues.
Другие товары поставщика
|
|
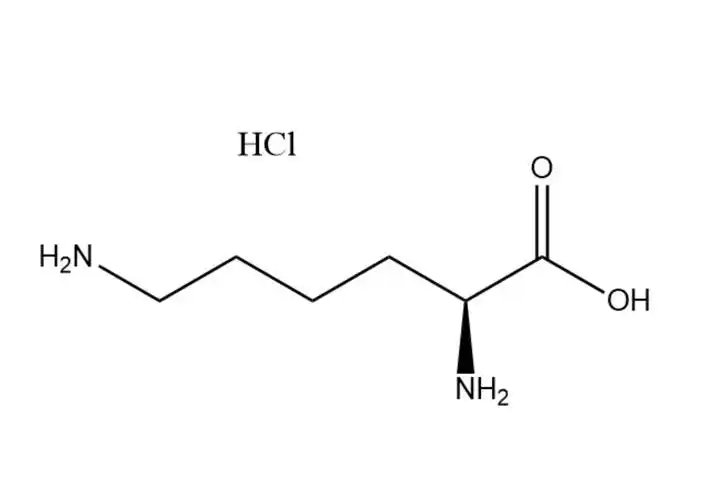
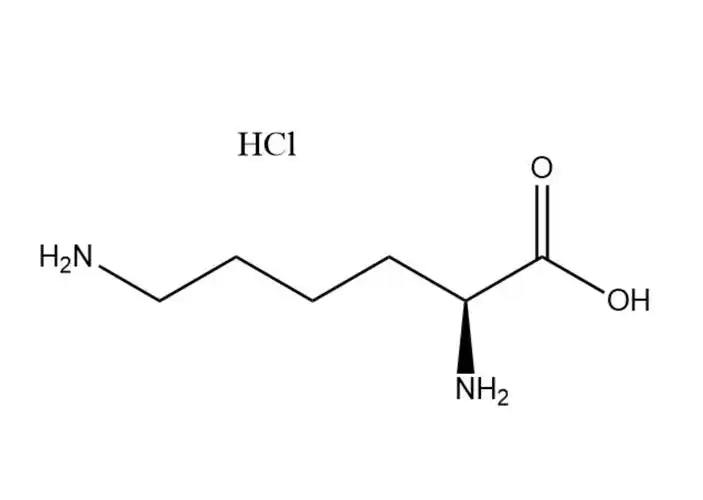
L-Lysine monohydrochloride |
L-Lysine monohydrochloride (molecular formula: C6H14N2O2⋅HCl, CAS No.: 657-27-2) is the hydrochloride salt form of L-lysine—an essen... |
|
|
L-tryptophan |
L-tryptophan’s physical and chemical properties—rooted in its indole ring structure and amphoteric nature—dictate its stability, ... |
|
|
L-Lysine monohydrochloride |
Density and Refractive Index of L-Lysine monohydrochlorideBulk density: 0.6–0.8 g/cm³ (crystalline powder); tap density: 0.8–1.0 g... |
|
|
DL-methionine |
The methylthio group is the most distinctive functional group in DL-methionine and can participate in substitution and addition reactions. Alkylati... |
|
|
L-leucine |
Basic InformationChemical Formula: C6H13NO2Molecular Weight: 131.17 g/molStructure: It has a branched - chain structure with a carboxyl group (-COO... |
Все товары поставщика
Похожие товары