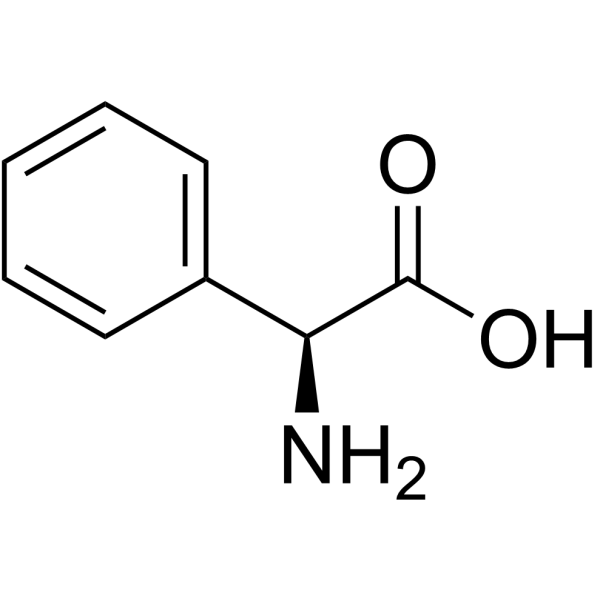
L-Threonine


L-Threonine is an essential amino acid with specific physical properties that influence its behavior in biological systems and industrial applications. Below is a detailed breakdown of its physical characteristics: 1. Molecular Structure and Formula IUPAC Name: (2S,3R)-2-Amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid Chemical Formula: C49NO3 Molecular Weight: 119.12 g/mol Stereochemistry: L-Threonine has two chiral centers (at carbon 2 and 3), giving it four stereoisomers. The biologically active form is (2S,3R), which has a hydroxyl group on the β-carbon (C3) and an amino group on the α-carbon (C2). 2. Physical State and Appearance Solid Form: White to off-white crystalline powder Crystal Structure: Monoclinic crystals (under standard conditions) Odor and Taste: Odorless, with a slightly sweet taste 3. Solubility and Physical Constants Water Solubility: Highly soluble in water (approx. 20.5 g/100 mL at 25°C). Its polarity (from the amino, carboxyl, and hydroxyl groups) enables strong hydrogen bonding with water. Solubility in Organic Solvents: Poorly soluble in non-polar solvents (e.g., ether, chloroform) but slightly soluble in polar organic solvents like ethanol (approx. 0.5 g/100 mL at 25°C). Melting Point: 255–257°C (with decomposition). The high melting point reflects strong intermolecular interactions (hydrogen bonds and ionic interactions between amino and carboxyl groups). pH of Aqueous Solution: Neutral aqueous solutions of L-threonine have a pH around 5.9–6.1, but the pH can vary with concentration. 4. Optical Activity Specific Rotation: [α]₂₀ᴰ = -28.5° to -31.5° (in 1 M HCl solution). This indicates that L-threonine rotates plane-polarized light to the left (levorotatory) under standard conditions. Optical Purity: Natural L-threonine is optically pure, while synthetic forms may require resolution to obtain the L-isomer. 5. Ionization and Acid-Base Properties (1)pKa Values: α-Amino group (-NH3^+): pKa ≈ 9.10 α-Carboxyl group (-COOH): pKa ≈ 2.09 β-Hydroxyl group: Not ionizable under physiological conditions, but the hydroxyl can form hydrogen bonds. (2)Isoelectric Point (pI): Calculated as (pKa1 + pKa2)/2 = (2.09 + 9.10)/2 ≈ 5.60. At this pH, L-threonine exists as a zwitterion (NH3^+-CH(CHOHCH3)-COO^- ) with minimal net charge.
Другие товары поставщика
|
|
L-Cysteine hydrochloride monohydrate |
Hygroscopic Properties of L-Cysteine hydrochloride monohydrateL-Cysteine hydrochloride monohydrate readily forms hydrates or dissolves in absorbed ... |
|
|
α-Lipoic Acid |
Product Usage: Exogenous lipoic acid is reduced by two or more enzymes within the cell. This reduced form affects the cell's process of scavenging ... |
|
|
L-proline |
Basic informationStructural characteristics: The molecular structure of L-proline is rather unique. Its α -amino group is an imine, and the h... |
|
|
L-leucine |
L-leucine has a wide range of applications in the fields of medicine, food, and cosmetics, among others. The details are as follows:1.Medical Field... |
|
|
High quality |
Biological Role An essential amino acid for humans, meaning it must be obtained from the diet. Plays a role in protein structure (e.g., forming hyd... |
Все товары поставщика
Похожие товары