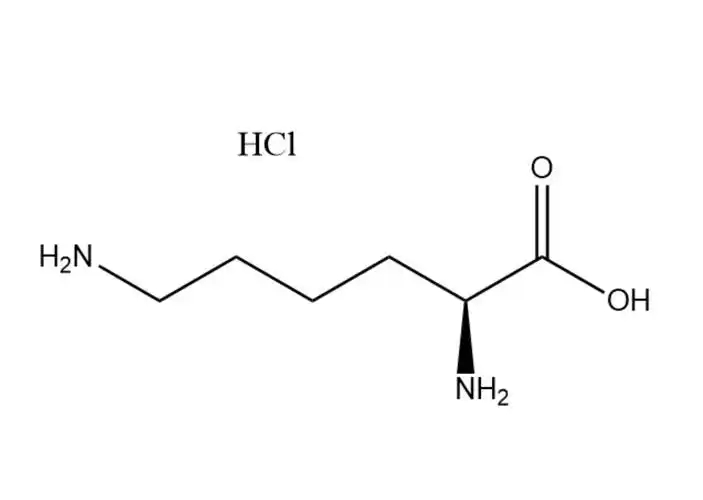
Magnesium Gluconate


Applications of Magnesium Gluconate
1. Nutritional Fortification in Food and Beverages
(1)Magnesium Supplementation: As a bioavailable magnesium source, it is added to:
Breakfast cereals, energy bars, and snacks to enhance mineral content.
Dairy products (yogurt, milk) and plant-based drinks (soy, almond milk) for fortification.
Infant formulas and toddler foods to meet daily magnesium requirements (e.g., 30–75 mg/day for infants).
(2)Functional Foods: Used in “bone-health” products alongside calcium and vitamin D, as magnesium is essential for bone mineralization.
(3)Sports Nutrition: Added to electrolyte drinks or recovery supplements to replace magnesium lost through sweat, supporting muscle function and energy metabolism.
2. Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical Formulations
(1)Oral Supplements:
Treats magnesium deficiency (hypomagnesemia), which can cause muscle cramps, fatigue, or arrhythmias.
Available as tablets, capsules, or oral solutions; its high solubility and low gastrointestinal irritation make it preferable to salts like magnesium oxide (which can cause diarrhea).
(2)Antacids and Gastrointestinal Agents:
Mild alkalinity helps neutralize stomach acid, relieving heartburn or indigestion.
Sometimes combined with antacids like calcium carbonate for enhanced efficacy.
(3)Parenteral and Topical Use:
Rarely used in injectable solutions (other salts like magnesium sulfate are more common), but its low toxicity allows potential use in specialized medical formulations.
Topical creams or lotions for magnesium absorption, though less common than transdermal magnesium chloride.
3. Animal Feed and Veterinary Applications
(1)Livestock and Poultry Nutrition:
Added to animal feed to prevent magnesium deficiency, which causes “grass tetany” in ruminants (cattle, sheep) or growth retardation in pigs and poultry.
Improves feed efficiency and bone development in young animals.
(2)Aquaculture: Used in fish feed to support osmoregulation and enzyme function in aquatic species.
4. Cosmetics and Personal Care Products
(1)Skincare Ingredients:
Incorporated into moisturizers, serums, or masks for its potential to:
Soothe irritated skin due to its mild alkaline nature.
Support skin barrier function by promoting electrolyte balance.
Found in “mineral-enriched” products targeting dry or sensitive skin.
(2)Hair Care: Added to shampoos or conditioners to strengthen hair follicles, though evidence for this use is limited.
5. Industrial and Technical Applications
(1)Chemical Synthesis:
Serves as a magnesium source in organic synthesis, e.g., for preparing magnesium-based catalysts or reagents.
Used in the production of gluconic acid derivatives or other metal gluconates (e.g., calcium gluconate).
(2)Electroplating and Surface Treatment:
Occasionally used in electroplating baths to improve the uniformity of metal coatings, though less common than inorganic magnesium salts.
(3)Water Treatment: As a chelating agent, it can sequester metal ions in water, preventing scale formation in industrial systems, though EDTA or other chelants are more typical.
6. Agriculture and Horticulture
(1)Fertilizers and Plant Nutrition:
Applied as a foliar spray or soil amendment to correct magnesium deficiency in plants, which causes yellowing leaves (chlorosis) in crops like citrus, tomatoes, or roses.
Its water solubility allows rapid absorption by plant roots or leaves.
(2)Post-Harvest Treatment: Coated on fruits (e.g., apples, bananas) to extend shelf life by inhibiting enzymatic browning and maintaining firmness.
7. Specialized Medical and Research Uses
Dialysis Solutions: In some formulations, magnesium gluconate adjusts magnesium levels in patients undergoing dialysis, where electrolyte balance is critical.
Cell Culture Media: Used in laboratory settings to supply magnesium for cell growth, as it is an essential cofactor for enzymes involved in DNA replication and protein synthesis.
Key Advantages Driving Its Applications:
High Solubility: Dissolves readily in water, enabling easy incorporation into liquids (e.g., beverages, injectables).
Low Reactivity: Stable in most food and drug formulations, with minimal impact on taste, color, or texture.
Bioavailability: Magnesium ions are efficiently absorbed, and the gluconate moiety is non-toxic and metabolically inert.
Mild pH Profile: Alkaline nature makes it suitable for neutralizing acids without causing harshness.
Magnesium gluconate’s versatility stems from its balance of chemical stability, biological safety, and functional properties, positioning it as a preferred magnesium source across industries from nutrition to cosmetics.
Other supplier products
|
|
Magnesium Citrate |
Highly soluble in water, which contributes to magnesium citrate's effectiveness as both a magnesium source and a laxative. Usually appears as a whi... |
|
|
Bulk supply Magnesium Citrate |
Magnesium is an essential mineral involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions, including energy metabolism, muscle contraction, nerve function, and bo... |
|
|
Magnesium Citrate |
Chemical Formula: C₄H₃NaO₄
It is formed by the partial neutralization of fumaric acid (HOOC-CH=CH-COOH), where one carboxyl group (-COOH) loses a ... |
|
|
Monosodium fumarate |
Monosodium fumarate, a sodium salt of fumaric acid, is primarily valued for its functional properties in various industries, with its most prominen... |
|
|
Magnesium Lactate Powder |
Magnesium lactate in Cosmetics and Personal Care Products Skin Care Ingredients: Moisturizer: Added to lotions, creams, and serums for its hydratin... |
供应产品
Same products