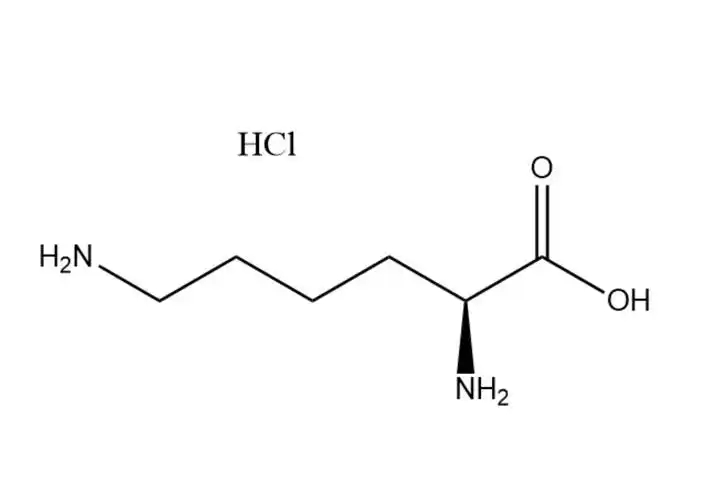
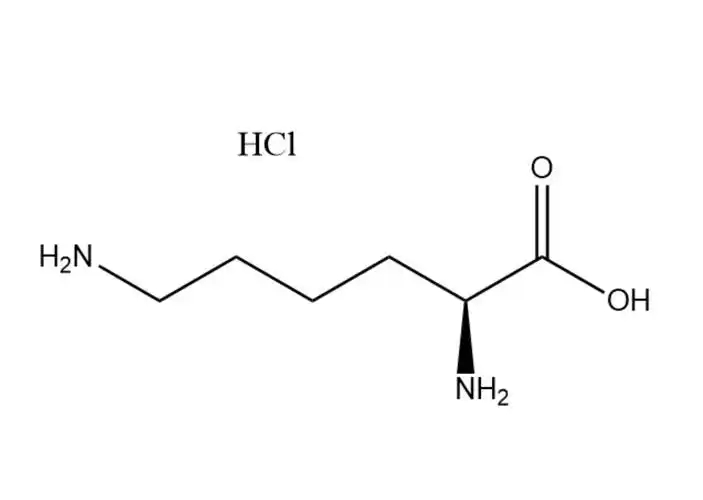
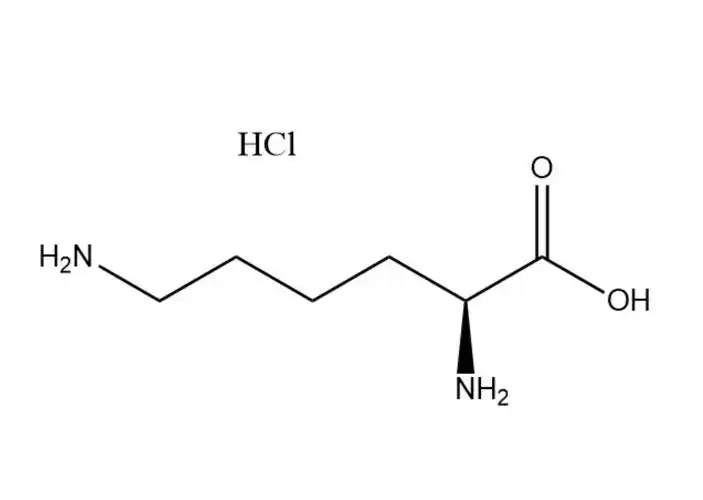
L-Lysine monohydrochloride
L-Lysine monohydrochloridehas a higher aqueous solubility than free L-lysine: ~70 g/100 mL at 25 °C (vs. ~63 g/100 mL for free L-lysine), with solubility increasing significantly with temperature (up to 110 g/100 mL at 60 °C). Its dissolution is rapid, endothermic, and free of precipitation in dilute to high-concentration aqueous solutions (up to 60% w/v). This advantage makes it ideal for:
- Liquid formulations (e.g., oral nutritional supplements, animal drinking water additives, pharmaceutical syrups) where high solubility and clear solutions are required.
- Industrial production processes (e.g., fermentation downstream purification, formulation blending) that demand fast dissolution and uniform dispersion in aqueous systems.
In contrast, free L-lysine has lower solubility and may form supersaturated solutions that precipitate during storage, leading to formulation instability.
Other supplier products
|
|
L-Methionine powder |
The sulfur-containing side chain of L-Methionine contributes to the structural integrity of keratin (the primary protein in skin, hair, and nails):... |
|
|
DL-Methionine |
Acid-Base Properties of DL-MethionineDL-Methionine is a neutral amino acid, and its acid-base behavior is derived from the amphoteric nature of the... |
|
|
DL-methionine |
The methylthio group is the most distinctive functional group in DL-methionine and can participate in substitution and addition reactions. Alkylati... |
|
|
High quality N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine |
N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine, often abbreviated as NAC, is a derivative of the amino acid cysteine. Here is a detailed introduction:
Basic Information
Chem... |
|
|
L-proline |
The biological functions of L-prolineProtein structure maintenance: L-proline is one of the 20 common amino acids that make up proteins. Its cyclic... |
供应产品
Same products