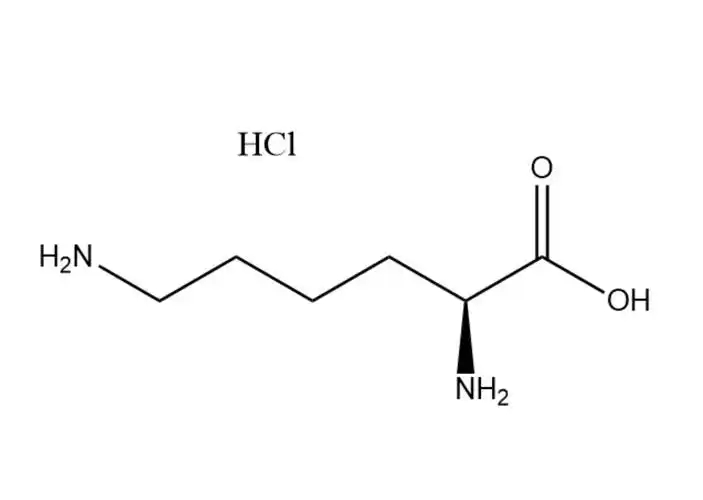
L-Aspartic acid monosodium salt monohydrate


To avoid unwanted chemical reactions or flavor changes, manufacturers must consider its compatibility with other food components: Avoid mixing with strong oxidizers: L-Aspartic acid monosodium salt monohydrate may react with oxidizing agents (e.g., some food preservatives like potassium sorbate) at high temperatures, leading to the breakdown of flavor compounds or the formation of off-tastes. Acidic matrices: While it acts as a buffer, in highly acidic foods (pH <2.5, e.g., citrus juices, vinegar-based dressings), L-Aspartic acid monosodium salt monohydrate may partially convert back to free L-aspartic acid (which is less soluble). This can cause cloudiness or sedimentation, so it is best used in foods with pH 3.0–7.0. Metal ions: L-Aspartic acid monosodium salt monohydrate may form weak complexes with divalent metal ions (e.g., Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺) in dairy or mineral-fortified foods, but this does not affect safety—only solubility. To prevent clumping, it should be dissolved in water before adding to milk or yogurt.
Other supplier products
|
|
Glycyl-glycine |
Glycyl-glycine provides support for metabolic health Emerging research suggests potential benefits in metabolic contexts: As a glycine precursor, g... |
|
|
Cystine Disodium Salt |
Cystine Disodium Salt, systematically named disodium (R,R)-3,3'-dithiobis(2-aminopropanoate), is a water-soluble ionic derivative of L-cystine&md... |
|
|
Glycylglycine |
As a simple dipeptide composed of two glycine molecules, glycylglycine (Gly-Gly) plays a critical role in peptide synthesis, stability, and bioacti... |
|
|
DL-tryptophan |
In biochemical and medical research, DL-tryptophan’s racemic nature offers unique advantages: Enantiomer Comparison Studies: It allows resear... |
|
|
Cystine Disodium Salt |
The disulfide bond (-S-S-) is the most reactive functional group in Cystine Disodium Salt, and its redox conversion with thiol groups (-SH) is a co... |
供应产品
Same products