Image Analysis
Dynamic Imaging Particle Analysis
Most particle size measurement techniquesmethods are based on the assumption of spherical shaped particles. This hypothesis leads to significant errors in the analysis if the particles are flake or rod-shaped. Especially for such highly form-anisotropic particles, automated imaging provides an excellent alternative for the determination of tailor-made size specifications.
Automated imaging methods for the determination of the particle size distribution of a material offers a fundamental advantage over alternative methods such as static light scattering, sedimentation or sieving: Each particle is photographed individually! This results in several important advantages for the determination of the particle size distribution:
Realistic proportional values also at the edges of the size distribution, i. e. detection of oversized particles or fine particles
Visual assessment of the dispersing state of a sample (dispersing quality, presence of agglomerates)
Calculation of meaningful size parameters, e. g. geodetic length or Feret diameter for fibres, depending on the application
Selection of the appropriate distribution type (volume, number) depending on the particular task
In addition, the individual photography of the particles gives the opportunity to make statistical calculations on the particle shape, which in practice enables further differentiation of materials. For example, form anisotropy, the deviation of the particles from the ideal sphere, often plays a decisive role for their application and further processing – for example, the conveyance or compaction of powders, the influence on the rheology in dispersions or, in addition to the particle size distribution, the roughness of the particle surface plays an important role for the success of shaping or polishing.
The necessity for tailor-made particle size and shape parameters, combined with ever-increasing PC processing power, ensures that automated imaging methods are becoming increasingly more relevant to a market which is 95% non-spherical..
Measurement method
The determination of the particle shape by automated imaging includes 4 basic steps:
The image taking is ensured by special digital cameras, if necessary in combination to a microscope, to enlarge the particles. The particles may be present neutral (e.g. on an objective) or in motion as well. The dispersing (separation) of particles is possible both in dry-mode (e.g. by simple conveying and riddling or by the usage of compressed air) but also in wet-mode in a solvent. An absolutely basic requirement to perform a successful particle shape analysis is high resolution, image sharpness, good sample dispersing resulting in measurement of individual particles and suitable enlargement. More explanation of this expression required etc. Image processing by appropriate software leads to upgraded pictures: for example isolated pixels and edging particles are eliminated, variations in brightness and signal noise are retouched and agglomerated particles are separated. The main part in object detection is image binarization, whereby every image pixel is assigned to a particle (black) or the background (white) using a threshold. The recognition of objects (particles) and feature attribution is realized by the software. In the last step, the classification, the particles are arranged in classes (e.g. size equivalent classes) on the basis of their attributed features (size and shape parameters).
Numerous size and shape parameters can be determined from the particles images by the appropriate software. Important size parameters are for example (CE) equivalent disc diameter Deq, maximum inscribed disc diameter Din, fiber length XLG (geodesic length) and fiber diameter XFD.
The equivalent disc diameter corresponds to the disc diameter of identical area to 2-D-projected particles, which is often used as size indicator for irregular shaped particles in process technology. On the contrary the maximum inscribed disc diameter of the 2-D-projected particle corresponds more or less to the sieve diameter. The geodesic length and the fiber diameter are suited very well for the characterization of fibers.
There are numerous and very application-specific shape parameters. The aim is to get extra morphological parameters in addition to particle size, whereby the particle characteristics can be better or basically described. Examples are “aspect ratio AD”, the ratio of length to width of the particles, “circularity ZK”, an indicator for particle deviation from the ideal circle and “concavity index C”, which reflects the ratio of area difference of convex envelope and area of the particle to convex envelope. Another important shape parameter is “perimeter”, which displays the particle coverage.
Now the price of particle size instrumentis affordable, if you have needs to buy any particle size analyzer instrument, please contact us.
在线联系供应商
Other supplier products
| BeDensi B1 | Bulk Density Tester BeDensi B1 bulk density testing equipment adopts natural deposition method. Its manufacturing standard meets the criterion of G... | |
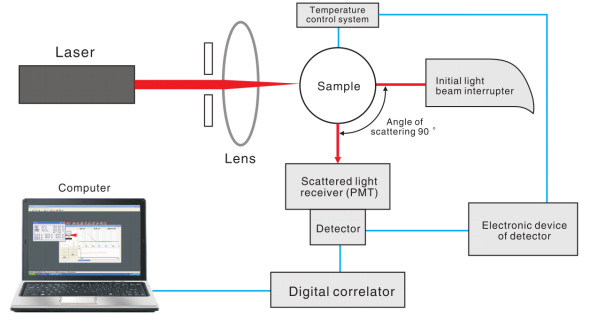
| Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) | Dynamic light scattering (DLS), also known as photon correlation spectroscopy (PCS), is a commonly used characterization method for nanoparticles. ... | |
| BeVision D2 | Dynamic Image Particle Analyzer with Dry Dispersion The BeVision D2 particle image analyzer(particle shape analyzer) is a microscopic image partic... | |
| Bettersizer 2600 | Bettersizer 2600 Laser Particle Size Instrument(Dry & Wet Dispersions) The Bettersizer 2600 utilizes this laser diffraction technology. The... | |
| BT-Online1 | Online Particle Size Analyzer BT-Online1 Online Particle Size Analyzer is an on-line particle size monitorsystem for real-time particle size monit... |