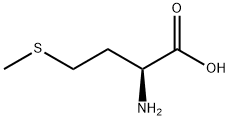
L-Methionine


L-Methionine accelerates tissue repair by: Promoting the synthesis of collagen and elastin, which form the structural framework of healing tissues (e.g., skin wounds, muscle injuries). Enhancing angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels) in the injured area, improving oxygen and nutrient delivery to support cell proliferation and tissue regeneration. Key Notes on Functional Regulation Synergy with other nutrients: L-Methionine’s functions depend on cofactors such as vitamin B6, folate, vitamin B12, and zinc, which are required for its activation (e.g., SAM synthesis) and metabolism (e.g., homocysteine conversion). A balanced diet ensures these synergistic effects. Avoidance of excess: While essential, excessive L-Methionine intake (e.g., >1g/day from supplements) can increase homocysteine levels, induce oxidative stress, or cause gastrointestinal discomfort (nausea, diarrhea). Individuals with liver or kidney disorders should use supplements under medical supervision, as impaired organ function may disrupt methionine metabolism.
Other supplier products
|
|
L-tryptophan |
L-tryptophan is naturally abundant in various protein-rich foods, with the following being key dietary sources: Animal products: Turkey, chicken, f... |
|
|
DL-Methionine |
Appearance and Crystal Morphology of DL-MethionineAt room temperature and normal pressure, DL-methionine exists as a white, odorless crystalline po... |
|
|
DL-Methionine |
DL-Methionine, chemically namedDL-2-amino-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid, is a racemic mixture composed of equimolar amounts of L-methionine and D-met... |
|
|
L-Methionine powder |
L-Methionine, as an essential sulfur-containing amino acid with diverse biological functions, has widespread applications across food nutrition, an... |
|
|
DL-Methionine |
Solubility of DL-MethionineWater solubility: DL-methionine isslightly soluble in water, which is a typical characteristic of non-polar amino acids.... |
供应产品
Same products
|
|
Easy-cleaning Silicone-Modified Waterborne UV Resin |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
LUV533 is a high-performance, silicone-modified hexafunctional waterborne UV resinengineered to d... |
|
|
Water-based Soft-Touch Resin for Consumer Electronics |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
Water-based Soft-Touch Resinis an advanced coating material formulated to deliver a luxurious, ve... |
|
|
Conformal Coatings |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
The conformal coatingsprovide good adhesion to metal, PCB and other substrates after curing at ro... |
|
|
Metalized & Laser Transfer coating |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
Metallized and laser transfer coatingsare designed with sustainability in mind, ensuring minimal ... |
|
|
Hydrophilic coatings for Air Conditioner |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
A water-based coating combination applied on the surface of aluminum foil, which forms a layer wi... |