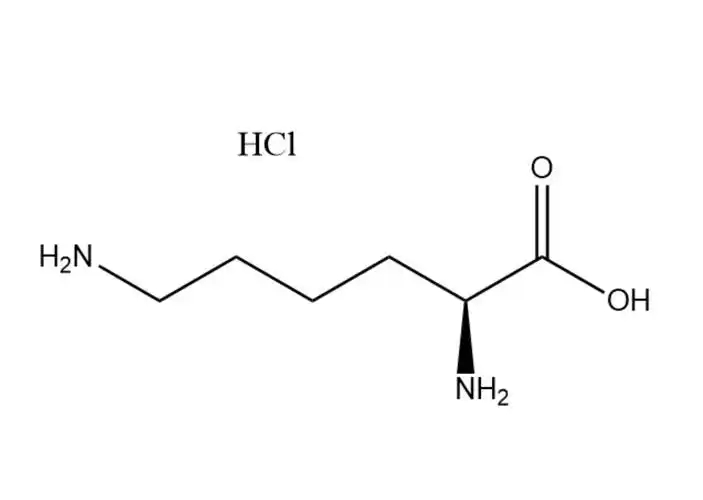
Calcium Carbonate Supply price
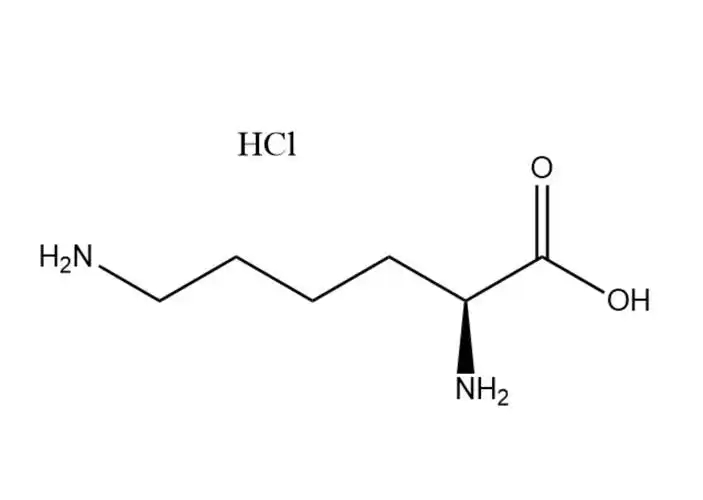
The molecular structure of Calcium Carbonate
It is formed by the combination of calcium ions (Ca²⁺) and carbonate ions (CO₃²⁻) through ionic bonds and belongs to ionic crystals.
It exists in nature in various crystal forms. Common ones include:
Calcite: Trigonal crystal system, with a compact crystal structure and a relatively high density (2.71g /cm³), is the most stable crystal form of calcium carbonate.
Aragonite: Orhombic crystal system, with a slightly higher density (2.93 g/cm³). Thermodynamically, it is less stable than calcite and can transform into calcite over a long period of time.
Vaterite: Hexagonal crystal system, rare, metastable crystal form, easily transforms into calcite or aragonite.
Other supplier products
|
|
Magnesium Citrate Purchase price |
In clinical settings, magnesium citrate is used to address specific health conditions: Electrolyte replacement: Administered orally (or intravenous... |
|
|
Monosodium Fumarate Market quotation |
While less common than its food uses, monosodium fumarate has limited roles in these fields: Excipient in Drug Formulations: It may act as a pH adj... |
|
|
Magnesium Gluconate Wholesale Price |
Melting Point and Thermal Stability of Magnesium Gluconate Melting Point: Decomposes rather than melts at high temperatures, with decomposition sta... |
|
|
Manganese Gluconate CAS 6485-39-8 |
Product Name:Manganese Gluconate Description Molecular formula:C12H22MnO14 • 2H2O Molecular weight:481.27 Manganese assay:11.43% Shelf life:24... |
|
|
calcium carbonate Partners, long-term cooperation |
During the transportation of calcium carbonate, its physical and chemical properties should be comprehensively considered to ensure its safe and ef... |
All supplier products
Same products