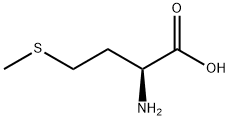
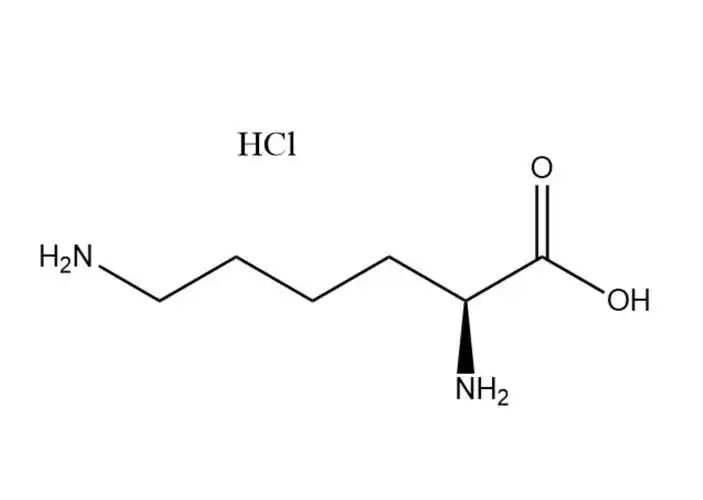
L-tryptophan
L-tryptophan is naturally abundant in various protein-rich foods, with the following being key dietary sources: Animal products: Turkey, chicken, fish (e.g., salmon, tuna), eggs, dairy (milk, yogurt, cheese) are among the richest sources. For example, 100 grams of turkey breast contains approximately 0.3 grams of tryptophan. Plant-based foods: Legumes (lentils, chickpeas), nuts and seeds (pumpkin seeds, almonds), whole grains (oats, quinoa), and some fruits and vegetables (spinach, bananas) also provide moderate amounts, though generally less than animal sources. These natural sources contribute to daily tryptophan intake, supporting basic physiological functions like protein synthesis and neurotransmitter production.
Other supplier products
|
|
L-Tyrosine |
Potential Benefits ·Improves mental clarity and cognitive performance. ·Enhances stress resilience and energy levels. ·Support... |
|
|
L-Threonine |
Physical Properties of L-Threonine Molecular Formula C₄H₉NO₃ (molecular weight: 119.12 g/mol). Appearance and State White to off-white crystalline ... |
|
|
Manufacturer |
Metabolism and Safety of L-Methionine L-Methionine is absorbed in the small intestine via amino acid transporters and metabolized primarily in the ... |
|
|
DL-Methionine |
Solubility of DL-MethionineWater solubility: DL-methionine isslightly soluble in water, which is a typical characteristic of non-polar amino acids.... |
|
|
Fish collagen peptides |
Fish collagen peptides, also known as fish collagen or marine collagen, is a type of high-molecular-weight functional protein derived primarily fro... |
供应产品
Same products