Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
Dynamic light scattering (DLS), also known as photon correlation spectroscopy (PCS), is a commonly used characterization method for nanoparticles. The DLS particle size analyzerhas the advantages of accuracy, rapidity, and good repeatability for the measurement of Nano particles, emulsions or suspensions. BeNano 90 Zeta nano particle size analyser is a typical nanoparticle size measurement instrument based on dynamic light scattering.It can measure nanomaterial down to 1 nanometer which is an essential tool for nanoparticle size distribution measurement to understand and research nano powdered materials.
Theoretical background
What is light scattering? When a monochromatic and coherent light source irradiates onto the particle, the electromagnetic wave will interact with the charges in atoms that compose the particle, and thus induce the formation of an oscillating dipole in the particle. Light scattering refers to the emission of light in all directions from oscillating dipole. During quasi-elastic light scattering, the frequency changes between scattered light and incident light are small, and the light scattered by the oscillating dipole has a spectrum that broadens around the incident light frequency.
The scattered light intensity depends on the particle's intrinsic physical properties such as size and molecular weight. The scattered light intensity is not a constant value; it fluctuates over time due to the random walk of particles that are undergoing Brownian motion which refers to the particle's continuous and spontaneous random walk when placed in the medium resulting from the collisions between the particles and the medium molecules. The fluctuations in scattered light intensity with time allows us to calculate the diffusion coefficient through the auto-correlation function analysis. To quantify the speed of Brownian motion, the translational diffusion coefficient is modelled by the Stokes-Einstein equation. Notice here the diffusion coefficient is specified by the word “translational”, indicating that only the translational, but not the rotational movement of the particle is taken into account. The translational diffusion coefficient has the unit of area per unit time, where the area is introduced to prevent the sign change convention when the particle is moving away from its origin. Then using the Stokes – Einstein equation, the particle size distribution can be calculated from the diffusion coefficient. This technique is called the dynamic light scattering, abbreviated as DLS.
Hydrodynamic radius refers to the effective radius of a particle that has identical diffusion to a perfectly spherical particle of that radius. For example, as seen in figure 1, the true radius of the particle refers to the distance between its center and its outer circumference, while the hydrodynamic radius includes the length of the attached segments since they diffuse as a whole. Hydrodynamic radius is inversely proportional to the translational diffusion coefficient.
Applications
By analyzing the fluctuating scattered light intensity due to Brownian motion, DLS can obtain the particle size distribution of small particles suspended in a diluted solution. Typically, the measuring size limit of DLS falls in the nano and sub-micro range, with the magnitude of 1 nanometer to 10 micrometers. There are several advantages of using the DLS when sizing particles. First, DLS is non-invasive to the samples, meaning that the structure of the molecules would not be destroyed during sizing. A small amount of sample is sufficient for a diluted solution preparation. With the DLS method, results with great repeatability and accuracy can be obtained within a few minutes. The testing process is nearly all automatic, minimizing operation errors from different operators. With DLS, the particle size distribution can be measured at different temperatures, and thus a thermal analysis can be conducted on the test sample. DLS provides various industries the opportunity to control their products' quality and therefore maximizing product performance by controlling particle size. These industries include but are not limited to semi-conductors, renewable energy, pharmaceuticals, inks, pigments, batteries, et cetera.
Optical Setup
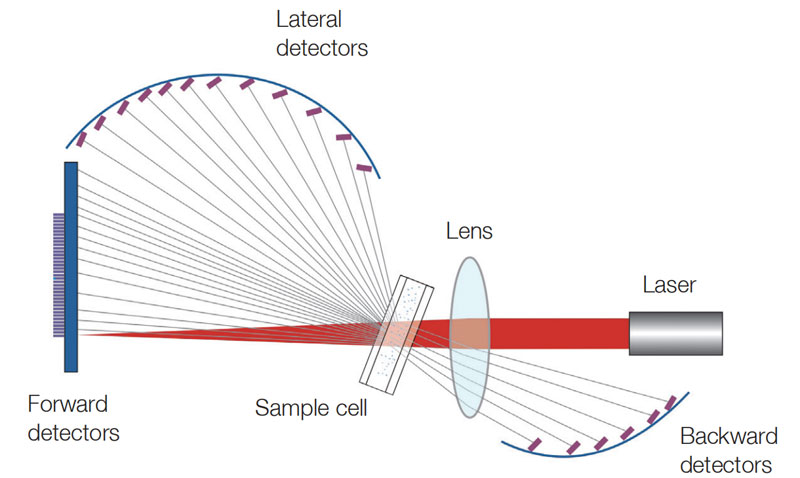
The whole setup of DLS instrument is shown in Figure 2.
•Laser
The majority of the laser devices in DLS instruments are gas lasers and solid-state lasers. Typical example of gas laser in DLS setup is helium-neon laser which emits laser with a wavelength of 632.8 nm. A solid-state laser refers to a laser device where a solid act as the gain medium. In a solid-state laser, small amounts of solid impurities called “dopant" are added to the gain medium to change its optical properties. These dopants are often rare-earth minerals such as neodymium, chromium, and ytterbium. The most commonly used solid-state laser is neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet, abbreviated as Nd: YAG. Gas laser has the advantages of stable wavelength emission with relatively low cost. However, a gas laser usually has a relatively large volume that makes it very bulky. On the other hand, a solid-state laser is smaller in size and also less heavy, making it more flexible to handle.
Scotti, A.; Liu, W.; Hyatt, J. S.; Herman, E. S.; Choi, H. S.; Kim, J. W.; Lyon, L. A.; Gasser, U.; Fernandez-Nieves, A. The CONTIN Algorithm and Its Application to Determine the Size Distribution of Microgel Suspensions. The Journal of Chemical Physics 2015, 142 (23), 234905.
At Bettersize, we provide particle size analyzer instrument, dynamic light scattering system, dynamic light scattering equipment, dynamic light scattering particle size analysis, particle size instrument, etc. Bettersize is here to provide you the better particle size solutions, and beyond.
在线联系供应商
Other supplier products
| BT-Online1 | Online Particle Size Analyzer BT-Online1 online particle size measurementis an on-line particle size monitoring system for real-time particle si... | |
| Bettersizer 2600 | Laser Particle Size Analyzer(Dry & Wet Dispersions) The integrated and robust laser particle size analyzer, Bettersizer 2600, can deliver reli... | |
| Particle Shape | Founded in 1995, Bettersize is China’s No. 1 player in laser particle sizingbusiness, in the most recent years. At Bettersize, our mission is... | |
| HFlow 1 | Metal Powder Flowability Tester HFlow-1 tests the flowability of metal powder by measuring whether the sample can flow through the 2.5mm standard f... | |
| Bettersizer ST | Laser Particle Size Analyzer, Laser Granulometry Bettersizer ST laser scattering particle size distribution analyzerincludes the patented Dual Lens... |
Same products
| Waste Aluminum Plastic Pyrolysis Plant | 卖方: Shangqiu Sihai Energy Technology Co.,Ltd | Waste Aluminum Plastic Pyrolysis Plant The refining of waste aluminum and plastic mainly uses a ... | |
| Continuous Tire/ Rubber Powder Pyrolysis Plant | 卖方: Shangqiu Sihai Energy Technology Co.,Ltd | Continuous Tire/ Rubber Powder Pyrolysis Plant Pyrolysis is the process of heating organic mater... | |
| Herbicide Supplier | 卖方: HEBEI LAIKE BIOTECH CO.LTD | Herbicide Supplier Wholesale Herbicide Suppliers - Laike Biotech is a professional supplier ... | |
| Press Fit Machine | 卖方: Guangzhou Top-leading Intelligent Technology Co.,Ltd | Press Fit Machine Mainly used in the semiconductor packaging industry, it can be used for variou... | |
| Tri-Temperature Test Product | 卖方: Guangzhou Top-leading Intelligent Technology Co.,Ltd | Tri-Temperature Test Product Mainly used in the semiconductor packaging industry, it can be used... |