L-Threonine 72-19-5
Thermal and Chemical Stability of L-Threonine
Heat Resistance: Stable under normal storage conditions but decomposes near its melting point. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures (e.g., above 100°C) can cause degradation, especially in the presence of moisture.
pH Stability: Relatively stable in neutral to slightly acidic/basic solutions but may degrade in strongly acidic (pH < 2) or basic (pH > 10) conditions over time.
Oxidation Sensitivity: The hydroxyl group on the β-carbon makes L-threonine slightly susceptible to oxidation under harsh conditions, though it is more stable than amino acids with thiol groups (e.g., cysteine).
Other supplier products
|
|
L-Threonine Market quotation |
L-Threonine Improves Food Texture and Functionality Dough Conditioner in Baking: Enhances gluten network formation, improving dough elasticity and ... |
|
|
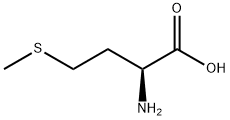
High quality DL-Methionine |
DL-Methionine, chemically designated asDL-2-amino-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid, is a racemic mixture consisting of equimolar quantities of L-methion... |
|
|
Fish collagen peptides Supplier |
Fish collagen peptides, also known as fish collagen or marine collagen, is a type of high-molecular-weight functional protein derived primarily fro... |
|
|
L-Threonine Manufacturer |
Industrial and Practical Implications Food and Feed Additives: L-Threonine’s solubility and stability make it suitable for fortifying foods a... |
|
|
L-Threonine Raw Material |
L-Threonine is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory bodies like the FDA when used in food at typical fortification levels. Its use mus... |
All supplier products
Same products