Manufacturer


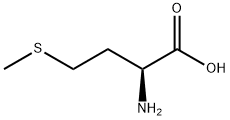
Metabolism and Safety of L-Methionine L-Methionine is absorbed in the small intestine via amino acid transporters and metabolized primarily in the liver. Its metabolic pathways include protein synthesis, transsulfuration (to cysteine and GSH), and remethylation (recycling to methionine). Excess methionine is catabolized to carbon dioxide, sulfuric acid, and urea, which are excreted from the body, with no significant accumulation under normal intake levels. In terms of safety, L-Methionine has a high margin of safety. The FAO/WHO recommends a daily intake of 13 mg/kg body weight for adults, and no adverse effects have been reported at doses within this range. However, excessive supplementation (exceeding 1000 mg/day for long periods) may lead to hyperhomocysteinemia, which is associated with increased cardiovascular risk, or gastrointestinal discomfort (e.g., nausea, diarrhea). Individuals with liver or kidney disorders should use it under medical supervision, as impaired organ function may affect methionine metabolism.
Other supplier products
|
|
DL-methionine |
The methylthio group is the most distinctive functional group in DL-methionine and can participate in substitution and addition reactions. Alkylati... |
|
|
Glycine |
Glycine is the simplest type of α-amino acid and is the only natural amino acid without a chiral carbon atom. Its molecular formula is C₂H₅NO... |
|
|
Glycine |
The main physiological functions of Glycine1. Synthesis of proteinsGlycine is one of the basic units that constitute the majority of proteins and i... |
|
|
L-Lysine monohydrochloride |
Appearance and Crystallinity ofL-Lysine monohydrochloride
Pure state: White, odorless, crystalline powder or prismatic crystals (orthorhombic ... |
|
|
L-Phenylalanine Manufacturer |
Uses of L-Phenylalanine 1. Precursor to Neurotransmitters: ·Dopamine: L-Phenylalanine is converted into tyrosine, which in turn is used to p... |
供应产品
Same products
|
|
Easy-cleaning Silicone-Modified Waterborne UV Resin |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
LUV533 is a high-performance, silicone-modified hexafunctional waterborne UV resinengineered to d... |
|
|
Water-based Soft-Touch Resin for Consumer Electronics |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
Water-based Soft-Touch Resinis an advanced coating material formulated to deliver a luxurious, ve... |
|
|
Conformal Coatings |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
The conformal coatingsprovide good adhesion to metal, PCB and other substrates after curing at ro... |
|
|
Metalized & Laser Transfer coating |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
Metallized and laser transfer coatingsare designed with sustainability in mind, ensuring minimal ... |
|
|
Hydrophilic coatings for Air Conditioner |
卖方: Guangzhou Human New Material Science and Technology Co., Ltd |
A water-based coating combination applied on the surface of aluminum foil, which forms a layer wi... |