L-leucine


L - leucine has several notable performance characteristics related to its physical and chemical properties, as well as its role in biological systems: 1.Physical and Chemical Properties White Crystalline Powder: It appears as a white, odorless crystalline powder with a slightly bitter taste. This physical form makes it easy to handle and incorporate into various products, such as nutritional supplements and food fortification. Solubility: It is sparingly soluble in water, with a solubility of about 2.3 g/100 mL at 25 °C. It is nearly insoluble in ethanol and ether. This solubility profile allows for its use in both aqueous and non - aqueous systems, depending on the application. Stability: L - leucine is relatively stable under normal conditions. However, like other amino acids, it can be affected by extreme temperatures, pH, and the presence of certain chemicals. For example, high temperatures or strong acids and bases can cause degradation or denaturation. 2.Biological Functionality Essential Amino Acid: It is an essential amino acid for humans and animals, meaning it must be obtained from the diet. It plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, serving as a building block for polypeptides and proteins. It ensures the proper growth, maintenance, and repair of tissues and organs. Muscle Metabolism Regulation: It is particularly important in muscle metabolism. It stimulates muscle protein synthesis, which is vital for muscle growth, recovery, and maintenance, especially after exercise or in situations of muscle stress. It can also help reduce muscle protein breakdown, making it valuable for athletes, bodybuilders, and individuals recovering from injuries or surgeries. Blood Sugar Regulation: L - leucine can influence blood sugar levels. It can stimulate insulin secretion to some extent, which aids in the uptake of glucose by cells, helping to regulate blood glucose levels and maintain energy balance. Energy Source: Although not the primary function, L - leucine can be metabolized to provide energy under certain conditions. It is converted into acetyl - CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle to produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
Другие товары поставщика
|
|
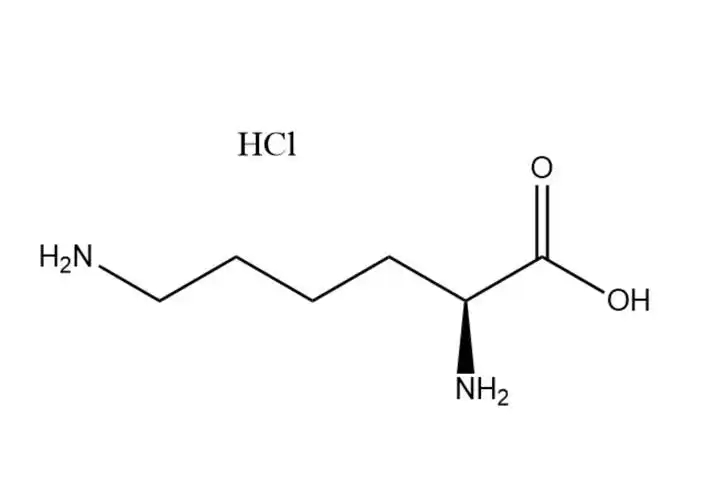
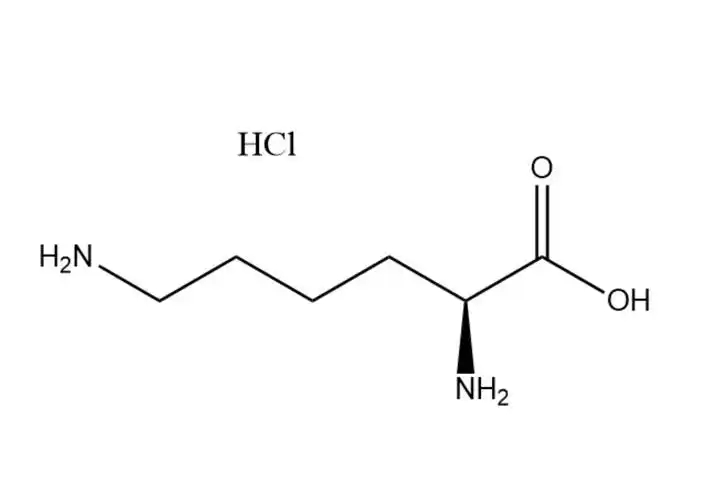
L-Lysine Monohydrochloride Price |
Reactions of Carboxyl and Amino Groups (Typical Amino Acid Reactions)
Neutralization reaction: Reacts with strong bases (e.g., NaOH, KOH) in a... |
|
|
α-Lipoic Acid |
Product Usage: Exogenous lipoic acid is reduced by two or more enzymes within the cell. This reduced form affects the cell's process of scavenging ... |
|
|
L-Glutamine |
L-Glutamine is a conditionally essential amino acid with important roles in the body. Here's a detailed introduction:
1. Chemical structure and na... |
|
|
L-Tryrosine |
L-Tryrosine is a non-essential amino acid that plays important roles in the human body. Here is a detailed introduction:
Basic Information
Chemica... |
|
|
L-Lysine monohydrochloride |
L-Lysine monohydrochloridehas a higher aqueous solubility than free L-lysine: ~70 g/100 mL at 25 °C (vs. ~63 g/100 mL for free L-lysine), with ... |
Все товары поставщика
Похожие товары