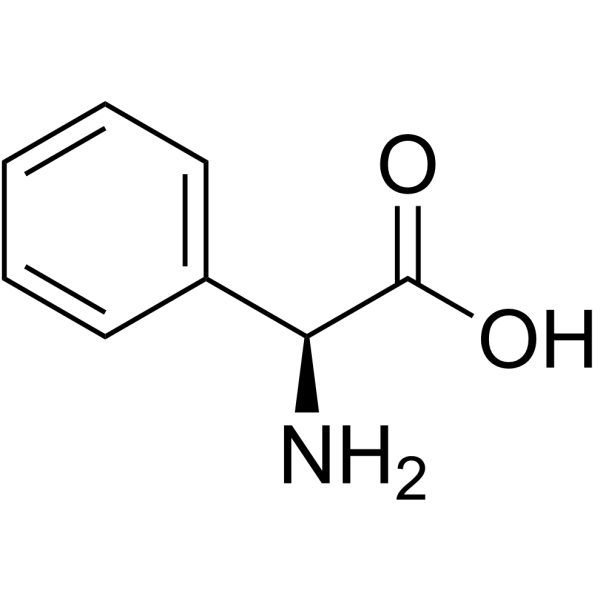
L-proline
The biological functions of L-proline
Protein structure maintenance: L-proline is one of the 20 common amino acids that make up proteins. Its cyclic structure can affect the secondary structure of proteins, causing a turn in the direction of polypeptide chains and playing a key role in the structural formation and stability of proteins such as collagen. Collagen contains a large amount of proline and hydroxyproline, which are crucial for maintaining the triple helix structure and stability of collagen.
Participation in biological metabolism: In organisms, proline is involved in multiple metabolic pathways. It can serve as an energy source and provide energy for cells through a series of metabolic reactions. In addition, proline is also involved in processes such as nitrogen metabolism and osmotic pressure regulation.
Other supplier products
|
|
DL-Alanine |
DL-Alanine is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory bodies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safet... |
|
|
High quality |
Beyond natural occurrence, L-tryptophan is sometimes added to fortified foods and functional products to enhance nutritional value or provide speci... |
|
|
Chemical |
L-Methionine plays a pivotal role in maintaining liver function and preventing lipid accumulation: It promotes fatty acid oxidation: By supporting ... |
|
|
DL-Alanine Powder |
DL-Alanine is a low-risk material for microbial growth (due to its amino acid nature, it is not a preferred nutrient for most spoilage microbes und... |
|
|
L-proline |
Storage and transportation of L-prolineStorage conditions: Store in a sealed container in a cool and dry place, away from moisture, high temperatur... |
供应产品
Same products